difference between autoclaving and sterilization|autoclave steam sterilization process : importing The terms autoclave and sterilizer are often used interchangeably. Yet, noting their distinctions from each other remains important for intended applications. Ultimately, the right choice of medical sterilizer or autoclave machine depends on the size and . See more The purpose of this research is to evaluate the supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO 2) sterilization-based NovaClean process for decontamination and reprocessing of personal .Adhesives have been used in the medical market for nearly three decades. Although a number of adhesives are industrially available, not all possess biocompatibility compliance. Cyanoacrylate, light curing cyanoacrylate, light curing acrylic, dual UV/moisture curable silicone, epoxy and urethane adhesives . See more
{plog:ftitle_list}
If you have a tattoo salon, the best autoclave to choose is autoclave with superheated steam. They have the highest temperature level of processing, which speeds the .
At the core, both autoclaves and sterilizers are sterilization devices used for disinfecting medical equipment. The main difference between autoclaves and sterilizers lies in . See more
Conversely, a sterilizer refers to a device that can sterilize small pieces of equipment needed for medical applications. An autoclave falls under this category term. Basically, all autoclaves are a type of sterilizer, but not all sterilizing systems are . See moreThe terms autoclave and sterilizer are often used interchangeably. Yet, noting their distinctions from each other remains important for intended applications. Ultimately, the right choice of medical sterilizer or autoclave machine depends on the size and . See more
The two basic types of steam sterilizers (autoclaves) are the gravity . Sterilization can be sometimes tricky and unpredictable. While some choose to boil their equipment, most professionals would rather use steam sterilization by either a pressure cooker or a steam sterilizer (or autoclave). Sterilization is a procedure used to kill or physically remove microorganisms and their various resistant reproductive spores.
Definition of Terms. Sterilization describes a process that destroys or eliminates all forms of microbial life and is carried out in health-care facilities by physical or chemical methods. Steam under pressure, dry heat, EtO gas, hydrogen peroxide gas plasma, and liquid chemicals are the principal sterilizing agents used in health-care facilities. Read on to learn more about the differences between disinfecting and sterilizing, and about some best practices for fighting COVID-19 and other harmful agents. What it means to disinfect vs. sterilize Sterilization Methods: The different methods used for sterilization are discussed below: Steam Sterilization: Steam Sterilization also refers to autoclaving, it involves exposing a specific product or surface to high-temperature steam (between 121-134°C) for a specific period range. The combination of high temperature and pressure of the steam . A Closer Look at an Autoclave. Many use the terms autoclave and steam sterilization synonymously, but an autoclave applies to medical tools, and steam sterilization can apply to anything in need of sterilizing. Autoclaves apply a steam sterilization method to eradicate harmful spores, bacteria, viruses, and fungi on vital tools and instruments.
Sterilization. Most medical and surgical devices used in healthcare facilities are made of materials that are heat stable and therefore undergo heat, primarily steam, sterilization. However, since 1950, there has been an increase in medical devices and instruments made of materials (e.g., plastics) that require low-temperature sterilization.
To understand the difference between sterilization and depyrogenation, we have to discuss both of them separately, in length to really know the line that separates them. Basically, sterilization is a method that can remove, kill and deactivate microorganisms on a surface like for example the stainless equipment, media etc. Sterilization Cycle Verification. A sterilization process should be verified before it is put into use in healthcare settings. All steam, ETO, and other low-temperature sterilizers are tested with biological and chemical indicators upon installation, when the sterilizer is relocated, redesigned, after major repair and after a sterilization failure has occurred to ensure they are . The World Health Organization recommends autoclave cycles run between 121 and 124 C for 15 minutes at about 30 PSI. This should be enough time to kill any microorganism. Autoclaves are common place in most labs and are an obvious choice for many applications. Drawbacks include overhead costs for the autoclave, as well as utility costs to run .
Autoclaves can carry out sterilization procedures on a variety of materials at the same time and in the fastest manner possible. Heat sterilizers are slower in the process of sterilization and , consequently, require longer to finish the task completely. Difference between hot air oven and autoclave Difference between hot air oven and autoclave pdf
Typical steam sterilization cycles are between 3 and 30 minutes at 121–134 °C (250–273 °F) at 100 kPa (15 psi), . Most autoclaves have meters and charts that record or display information, particularly temperature and pressure as a function of time. The information is checked to ensure that the conditions required for sterilization have . At constant temperatures, sterilization times vary depending on the type of item (e.g., metal versus rubber, plastic, items with lumens), whether the item is wrapped or unwrapped, and the sterilizer type. The two basic types of steam sterilizers (autoclaves) are the gravity displacement autoclave and the high-speed prevacuum sterilizer. Priorclave’s steam autoclaves can be custom configured to recreate any industrial sterilization method, without consuming the enormous volumes of water and energy necessitated by an industrial-sized retort. Whether it’s for food testing, lab quality and assurance, or product design analysis, a research and development autoclave can help you . Difference Between Sterilization and Sanitization. What is Sterilization? Definition: Sterilization is the process in which all microorganisms are either inactivated or are killed outright. . An autoclave can be used for equipment that is not heat sensitive. This instrument uses a combination of high temperature and pressure to kill microbes .
Autoclaves look like pressure cookers that use a process known as steam sterilization to kill foreign materials present in healthcare waste. Steam sterilization uses high-pressure and high-temperature steam that is well over 100 degrees Celsius (ranging between 121 and 134 degrees) to kill even heat-resistant bacteria. Sterilizing destroys bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi on surfaces. Typically, sterilization is used in the medical field; for example, surgical instruments are sterilized before use in an operating room, or dental instruments before a patient’s teeth cleaning. . difference-between-products-disinfect-sanitize-and-clean-surfacesSterilization: Sterilization can be physical (sterilization with heat, cold sterilization) or chemical (gas sterilization using chemical agents, cold chemical sterilization). Pasteurization: Depending on the temperature and the time the pasteurization can be Vat (batch) pasteurization (63°C for 30 minutes), HTST (72°C for 15 seconds), HHST .
amh elisa kits
Difference in sterilization methods. . Another difference between an autoclave and sterilizer relates to the materials. In a sterilizer, it is only possible to sterilize heat-resistant plastic. For example, it is not possible to sterilize rubber, compresses or hollow materials. In an autoclave, all instruments can be sterilized that qualify . Difference Between Autoclave and Dry Heat Sterilizer - Sterilization is a crucial process in the healthcare industry, food processing, and other related fields. It is a process that eliminates or kills all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and spores. Two common types of sterilizers are the autoclave and dry heat sterilizer. Autoclaves are used for the sterilization of contaminated instruments along with different culture media as it ensures complete sterility. Dry heat sterilization. . Difference Between (89) Diseases (32) Environmental Microbiology (11) Epidemiology (27) Food Microbiology (52) Genetics (79) The key to autoclaving is that the temperature must be high enough to kill endospores to achieve complete sterilization. Because sterilization is so important to safe medical and laboratory protocols, quality control is essential. Autoclaves may be equipped with recorders to document the pressures and temperatures achieved during each run.
All validated steam sterilization cycles provide efficacious autoclave sterilization when used according to manufacturer's instructions, but dynamic air removal cycles are preferred because they are more efficient than gravity cycles at removing air from the load. Anatomy of a Steam Sterilization Cycleo Selection of sterilization method o Difference between Aseptic Assembly and Terminal Sterilization • Sterilization using Irradiation o Gamma o E-Beam • Sterilization by Ethylene Oxide • Comparison between technologies • Distinguish disinfection, sterilization and decontaminationMaybe you’re still messing around with pasteurizing and sterilizing. It is normal. The sterilization and the pasteurization are thermal processes in which many factors come into play.. In general terms, we can say that both pasteurization and sterilization are conservation techniques that are based on the eradication of microorganisms and enzymes by applying heat for a certain time .
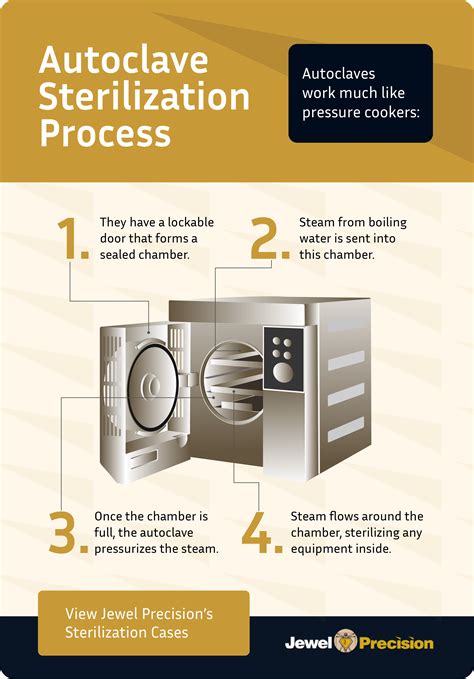
So this article is to know about the few, though important differences between the moist heat sterilization and dry heat sterilization. Content: Moist Heat Sterilization Vs Dry Heat Sterilization. Comparison Chart; Definition; . In this type of sterilization the autoclave is used, where the pressure of the steam with relatively high . Steam sterilization relies on three parameters to eliminate microbes and organisms: time, temperature, and pressure. These parameters can be manipulated into different cycles to meet the sterilization requirements of various types of loads, including red bags, media, glassware, cages, animal bedding, and pipette tips. Steam sterilization also referred as autoclaving is a method of cleaning objects making use of hot, humid gas (steam) to kill small bacteria that can cause us to get sick. . The key differences between dry heat sterilization and steam sterilization: Aspect Dry Heat Sterilization Steam Sterilization (Autoclaving) Principle:
sterilization procedure by autoclave

Steam sterilization has been used for decades and is by now a highly common method used for sterilizing items or goods that can withstand the moisture and the relatively high temperature .Sterilization autoclaves are widely used in microbiology and mycology, medicine and prosthetics fabrication, tattooing and body piercing, and funerary practice. They vary in size and function depending on the media to be sterilized and are sometimes called retort in the chemical and food industries. Typical loads include laboratory glassware, other equipment and waste, surgical instruments, and
difference between autoclaving and sterilization|autoclave steam sterilization process